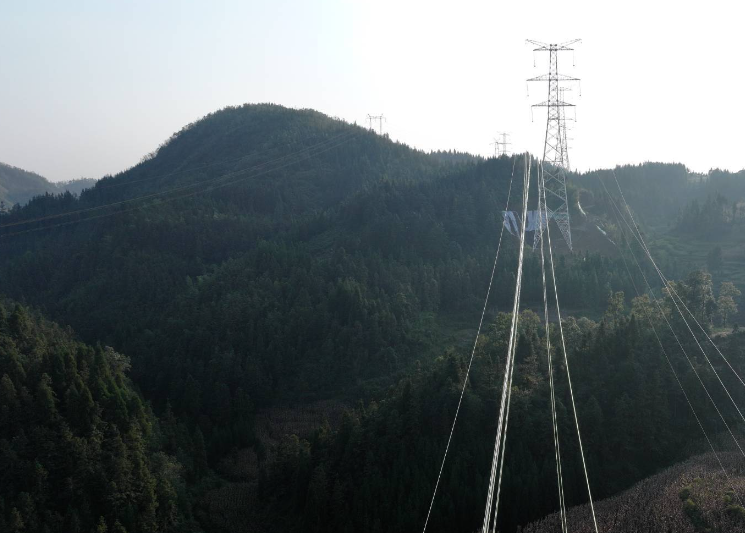
From a mechanical perspective, overhead transmission line conductors are subjected to their own gravity and the tension (tension) exerted by the towers at both ends. When the two ends of the wire are fixed on the tower, the wire will inevitably sag under the continuous action of gravity. According to the principles of material mechanics and statics, under the combined action of tension and gravity, a wire will take on the shape of a catenary, and sag is a physical quantity that describes the degree of sag of this shape. In reality, an increase in power load can also lead to an increase in sag.
一、 The role of sag in transmission line conductors:
1. Appropriate sag can ensure sufficient safety distance between the conductor and the ground, buildings, trees, and other obstacles. At different voltage levels, electrical equipment and circuits have corresponding insulation distance requirements. For example, for high-voltage transmission lines, it is necessary to ensure that the distance between the wire and the object below is large enough to prevent discharge in humid weather or when foreign objects come into contact with the wire, and to avoid short circuit accidents.
2. The sag affects the distance between wires of different phases. In three-phase transmission lines, a certain spatial distance needs to be maintained between each phase conductor to prevent adjacent phase conductors from contacting each other and causing phase to phase short circuits under wind swing, dancing, or other conditions. Appropriate sag can ensure good insulation performance between three-phase wires under normal operation and certain meteorological conditions.
3. The sag and wire tension are interrelated and are important parameters for ensuring mechanical safety. If the sag is too small, the tension of the wire will be too high, which may cause the wire to exceed its mechanical strength limit, resulting in broken strands or wires; On the contrary, excessive sag can cause the conductor to exert excessive tension on supporting structures such as towers, which may result in tower tilting, deformation, or even collapse.
二、 The necessity of monitoring
Meteorological conditions, wire temperature, aging and loss over time, construction damage, and foreign objects hanging on the wire can all lead to abnormal sag size. By monitoring the sag in real time, these abnormal changes can be detected over time and corresponding measures can be taken, such as adjusting wire tension, removing foreign objects, etc., to avoid accidents.
The Dingxin Smart Technology Transmission Line Sag Online Monitoring System DX-WPS100-HC uses sensors to measure sag, supporting direct measurement of wire sag or ground distance, as well as configuring functions such as wire tilt angle, temperature, tension, and image monitoring to achieve precise detection. The on-site data is transmitted in real-time to the monitoring center for storage and analysis, and the sag formula is used to calculate the status of wire sag and ground distance for power personnel to view.