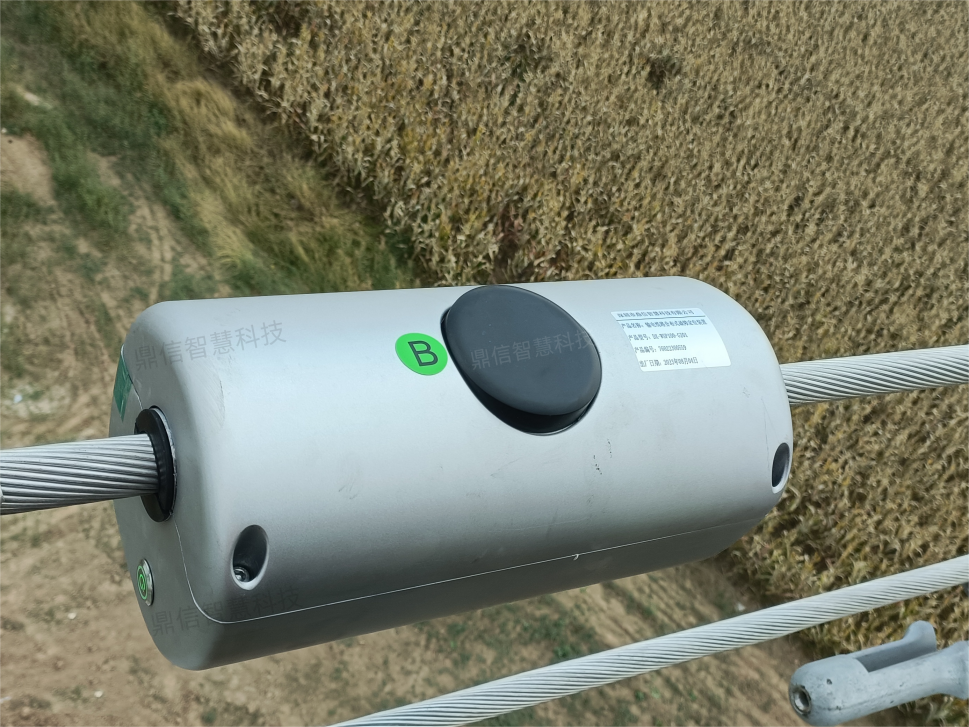
With the rapid development of the electric power industry and the continuous expansion of the power grid, the operating environment of transmission lines is becoming more and more complex, and the risk of failure also increases. In order to guarantee the continuity and reliability of power supply, our company has developed a transmission line Distributed Fault Diagnostic Device DX-WPS100-GZ01. Below, I would like to briefly explain the technical principle, technical requirements and algorithmic features of the device.
I. Technical principles
The technical principle of the distributed fault location device for transmission lines is mainly based on distributed traveling wave ranging technology, data communication technology and intelligent algorithms. By installing multiple monitoring terminals on transmission line conductors to achieve all-round coverage of the line, it can monitor real-time line traveling wave current, fault current waveform data, clock data, and quickly alarm when a fault occurs, locate the fault point, identify the type of fault, and reduce the time wasted in blind investigation. In addition, the monitoring terminal is connected to the monitoring platform center through wireless communication technology, which facilitates quick response and disposal of emergencies, and significantly improves the maintenance efficiency and power supply reliability of transmission lines.
II. Technical requirements
1. Devices and the full range of Internet of Things platform and its communication loop should be in line with the Q/CSG1204009 in the online monitoring system for power equipment security protection requirements;
2. Components installed on the line should take anti-vibration, anti-loosening measures, not wear and tear or other injuries to the conductor and ground, should not significantly reduce the phase-to-phase distance, the distance to the ground and to the electrical clearance of the tower, and to meet the design requirements;
3. Formal operation will not affect the operational safety of transmission lines.
III. Algorithmic features
1. Double-ended traveling wave ranging algorithm: double-ended traveling wave ranging is installed at both ends of the line are a set of monitoring terminals, through the detection of a traveling wave arrives at the two ends of the time difference to calculate the location of the fault point. Traveling wave ranging algorithm involves the identification of traveling waves, which contain a large number of high-frequency components, the measurement of the traveling wave head time point is an important factor affecting the ranging accuracy. Currently, the algorithm with higher accuracy is to use the phase mode transform to obtain the line mode components that are less affected by the line parameters, and then use the wavelet transform to identify the traveling wave head.
2. Deep Learning and Intelligent Algorithms: Deep learning techniques are used, especially Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Deep Belief Networks (DBN), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) and so on, and these models are able to extract higher-order, abstract, and detailed information about the fault features from a large amount of data, and classify the faults.
3. Automated Repair: Based on the type and cause of the failure, the system can The system provides targeted repair recommendations and assists technicians in troubleshooting.